Deploying a FastAPI application on a local cluster of Kubernetes
Deploying FastAPI on a local Kubernetes cluster is a great way to simulate production environments and ensure your API scales reliably. In this guide, we’ll walk through setting up FastAPI with Docker, creating Kubernetes manifests, and running everything on a local cluster using tools like Kind.

Step 1: Install tools
Install uv to create the project and manage dependencies:
https://docs.astral.sh/uv/getting-started/installationInstall Docker to manage docker images using Docker Desktop or Rancher Desktop or Podman:
https://docs.docker.com/get-started/get-docker/
https://docs.rancherdesktop.io/getting-started/installation/
https://podman.io/docs/installationInstall Kind to create the local cluster of Kubernetes
https://kind.sigs.k8s.io/docs/user/quick-start/Install kubectl command line tool to run command against Kubernetes clusters:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/toolsStep 2: Create a local cluster of Kubernetes using Kind
Create the following file kind.yaml in your test directory:
kind: Cluster
apiVersion: kind.x-k8s.io/v1alpha4
nodes:
- role: control-plane
kubeadmConfigPatches:
- |
kind: InitConfiguration
nodeRegistration:
kubeletExtraArgs:
node-labels: "CriticalAddonsOnly=true,eks-k8s-version=1.29"
extraPortMappings:
- containerPort: 30000
hostPort: 8000
protocol: TCP
- role: worker
kubeadmConfigPatches:
- |
kind: JoinConfiguration
nodeRegistration:
kubeletExtraArgs:
node-labels: "CriticalAddonsOnly=true,eks-k8s-version=1.29"
- role: worker
labels:
"CriticalAddonsOnly": "true"
"eks-k8s-version": "1.29"
We defined 1 control plane that is the brain of the Kubernetes cluster. It manages and orchestrates everything in the cluster. We also defined 2 worker nodes where our applications (containers/pods) actually run.
Create the cluster executing the following command (it could take 5 minutes depends on your pc):
kind create cluster --config kind.yaml --name cluster-testSet context to interact with your cluster:
kubectl config use-context kind-cluster-testGet the list of nodes in the cluster:
kubectl get nodes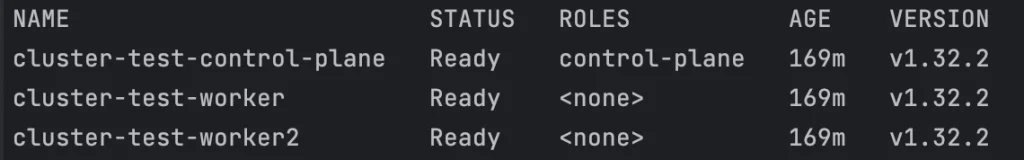
Step 3: create FastAPI app
In the same test directory execute the following command:
uv init test-apiAdd FastAPI dependency to the project:
cd test-api
uv add fastapi[standard]
Rename the hello.py to main.py and add this code:
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
@app.get('/')
async def hello_world():
return {
'status': 'OK',
'msg': 'Hello world!'
}
Step 4: create Dockerfile for the app
Add the Dockerfile in test-api directory:
# An example using multi-stage image builds to create a final image without uv.
# First, build the application in the `/app` directory.
FROM ghcr.io/astral-sh/uv:python3.12-bookworm-slim AS builder
ENV UV_COMPILE_BYTECODE=1 UV_LINK_MODE=copy
# Disable Python downloads, because we want to use the system interpreter
# across both images. If using a managed Python version, it needs to be
# copied from the build image into the final image; see `standalone.Dockerfile`
# for an example.
ENV UV_PYTHON_DOWNLOADS=0
WORKDIR /app
# Copy dependency files first for better layer caching
COPY pyproject.toml uv.lock ./
# Install dependencies
RUN --mount=type=cache,target=/root/.cache/uv \
uv sync --frozen --no-install-project --no-dev
# Copy the rest of the application code
COPY . .
# Install project dependencies
RUN --mount=type=cache,target=/root/.cache/uv \
uv sync --frozen --no-dev
# Then, use a final image without uv
FROM python:3.12-slim-bookworm
# It is important to use the image that matches the builder, as the path to the
# Python executable must be the same, e.g., using `python:3.11-slim-bookworm`
# will fail.
# Create the app user
RUN groupadd -r app && useradd -r -g app app
# Set the working directory
WORKDIR /app
# Copy the application from the builder
COPY --from=builder --chown=app:app /app /app
# Place executables in the environment at the front of the path
ENV PATH="/app/.venv/bin:$PATH"
# Run the FastAPI application by default
CMD ["uvicorn", "main:app", "--host", "0.0.0.0", "--port", "5000"]
Step 5: Build Docker Image
Execute the next command:
docker build -t test-api:v1.0.0 .Step 6: Push the Docker Image to the Kubernetes Cluster
Execute the following command:
kind load docker-image simple-api:v1.0.0Step 7: Deploy the app as a Kubernetes service
Create deployment.yaml in the main test directory:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: fastapi-app
labels:
app: fastapi
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: fastapi
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: fastapi
spec:
containers:
- name: fastapi
image: test-api:v1.0.0
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
ports:
- containerPort: 5000
env:
- name: UVICORN_LOG_LEVEL
value: "info"
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /docs
port: 5000
initialDelaySeconds: 5
periodSeconds: 10
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /docs
port: 5000
initialDelaySeconds: 10
periodSeconds: 20
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: fastapi-service
labels:
app: fastapi
spec:
selector:
app: fastapi
type: NodePort
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 5000
nodePort: 30000
The deployment manages and maintains a set of identical pods. It ensures your app is running and handles scaling, updates, and restarts automatically.
Create service.yaml in the main directory too:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: fastapi-service
labels:
app: fastapi
spec:
selector:
app: fastapi
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 5000
nodePort: 30000
type: NodePort
The service exposes a set of pods as a network service — internally or externally.
Step 8: create Makefile
Create the following Makefile in the main test directory:
# Variables
IMAGE_NAME=test-api
IMAGE_TAG=v1.0.0
CLUSTER_NAME=cluster-test
DEPLOYMENT_NAME=fastapi-app
DEPLOYMENT_FILE=deployment.yaml
DOCKERFILE=test-api/Dockerfile
.PHONY: all build kind-load deploy restart logs port-forward clean
# Build the Docker image
build:
cd test-api && docker build -t $(IMAGE_NAME):$(IMAGE_TAG) .
# Load image into kind cluster
kind-load:
kind load docker-image $(IMAGE_NAME):$(IMAGE_TAG) --name $(CLUSTER_NAME)
# Apply Kubernetes manifests
deploy:
kubectl apply -f $(DEPLOYMENT_FILE)
# Restart the deployment (forces new pods)
restart:
kubectl rollout restart deployment $(DEPLOYMENT_NAME)
# Tail logs of running pods
logs:
kubectl logs -l app=fastapi -f
# Port-forward service to localhost
port-forward:
kubectl port-forward service/fastapi-service 8000:80
# Full deploy pipeline
all: build kind-load deploy restart
# Delete everything (careful!)
clean:
kubectl delete all --all
Step 9: Test your app
Execute command:
make allCheck the app is working in:
You should see something like this:
{
"status": "OK",
"msg": "Hello world!"
}You have just deployed your FastAPI app in your local cluster of Kubernetes!
You can check all the code in my Github repository: